Muscle mass gain
There are three types of muscles in the human body – skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. All of our hollow organs, such as the intestines and stomach, have smooth muscles. Both the heart and smooth muscles are not subject to our will — they are "activated" by our autonomic nervous system.
In turn, we can almost completely control the activity of skeletal muscles . Next, we will talk about skeletal muscles, because if we can control them, we can also train them and shape them into the form we need.
The human body contains approximately 639 skeletal muscles, which make up 40 to 50 percent of our body weight.
Why approximately?
Because some of us may have some unique and unusual accessory muscles - therefore, the total number of muscles may increase or decrease.
Most skeletal muscles have names describing their features, such as size, shape, fiber direction, location, function… …
This makes their names easier to remember.
Muscle growth
Muscle growth is affected by our age, gender and genetics.
Muscle size increases when they are loaded.
Not just loaded, but overloaded - when they get an increased load when muscle fibers are damaged. The body repairs damaged fibers by merging them - this increases muscle mass and size.
Respectively - increasing the size, strength, and endurance of muscles is possible only by constantly increasing the load on them, for example - with strength training.
Hormones such as testosterone, growth hormone, and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), also play an important role in muscle growth and regeneration:
- Improving protein processing in our body;
- Inhibiting protein breakdown;
- Activating satellite cells - a kind of stem cells, which play an important role in muscle development;
- Stimulates anabolic hormones, which promotes muscle growth and protein synthesis;
- Promoting tissue growth.
Strength and resistance training helps our body:
- Release growth hormone from the pituitary gland;
- Stimulate testosterone release;
- Improve muscle sensitivity to testosterone.
Do muscles grow equally in men and women?
How quickly each individual can develop their muscles is affected by a number of factors, including genetics and estrogen and testosterone levels in the body.
Although muscle structure is exactly the same for men and women, it is much more difficult for women to build muscle. This is due to the different anatomy of both sexes, for example, men are "supposed" to have more muscle mass, bigger and longer bones and stronger joints, and genetics, such as different testosterone levels.
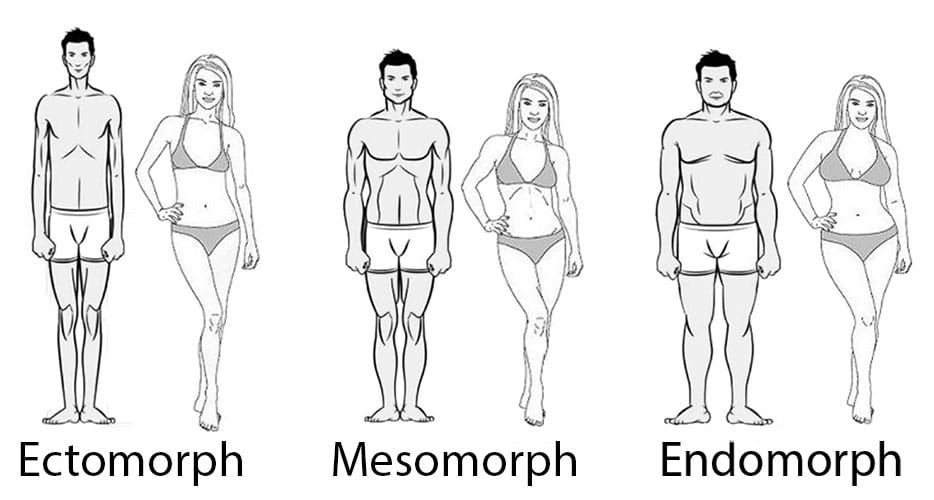
In both women and men, the rate of muscle growth largely depends on the specific body type:
- Ectomorphic (asthenic) body type. Ectomorphs have no pronounced muscle mass and no subcutaneous fat. They are naturally long and slender, the shoulders and chest are narrow, the bones are thin and the limbs are elongated. They are energetic and active, but they lack strength and endurance. Ectomorphs are less likely to build muscle mass, but they can increase their muscle strength with resistance/strength training.
- Mesomorphic (normosthenic) body type. Mesomorphs are characterized by well-developed musculature. The bones are medium in size, and the arms and legs are proportional to the body. Fat is evenly distributed throughout the body and does not accumulate at any specific part of the body. Mesomorphs are usually able to build muscle much faster than people with other body types;
- Endomorphic (hypersthenic) body type. Endomorphs have a pronounced layer of subcutaneous fat and their body stores fat faster. The body structure of these people is round with a tendency to fullness. People with an endomorphic body are endowed with natural strength and endurance and therefore can build muscle mass effectively through resistance/strength training.
It should be noted that there are relatively few people with one pronounced body type - we are all unique and constantly changing, and usually, we are a combination of two body types, for example:
- Ecto-endomorphic body type with a narrower upper body and accumulation of fat in the lower body;
- Endo-ectomorphic body type with narrower hips, thighs, and legs and more fat accumulation in the upper body.
But.
Do not confuse body type with body shape:
- Apple - round with a wider waist (for example - Endo-ectomorphic body type);
- Pear - with wider hips, buttocks and thighs (for example - ecto-endomorphic body type);
- Hourglass - with a narrow waist and more evenly distributed fat;
- Inverted triangle - with wider shoulders and chest;
- Ruler - body without pronounced curves.
Both men and women can have different body types, and each requires a different approach to building muscle.
Experience shows that any body can be changed, if you really want it.
Strength training and muscle building
Strength training is the most suitable for building muscle. However, cardiovascular and respiratory systems also need to be developed/trained to achieve better results and improve overall health.
The rate of muscle formation increases significantly if strength training is:
- Regular - at least 20 to 30 minutes, 2 to 3 times a week;
- Challenging enough - the muscles must work with a greater load than they are used to, and the load must constantly increase;
- Long-term - muscle grows slowly. The changes become visible no sooner than after 2 to 3 months.
The best results are achieved if there is enough rest time after training to allow the muscles to recover and grow. That is, training every day will not promote faster muscle growth.
Strength training
With muscles, everything is quite simple - Use them or you will gradually lose them.
This is also one of the reasons why muscle mass decreases with age - older people move less.
If the muscles are not used regularly, their mass will decrease (metabolism will slow down), but fat mass will increase.
Strength training can not only help maintain but also increase muscle mass at any age.
Strength training helps to:
- Strengthen bones - increase bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis;
- Maintain, increase or decrease weight as your muscles grow and metabolism accelerates;
- Protect joints from injury;
- Reduce the symptoms of many chronic diseases, such as arthritis, back pain, obesity, heart disease, depression and diabetes;
- Improve balance and reduce the risk of falls. This is particularly important for older people, as it helps them to remain independent for longer;
As a result, your ability to perform daily activities increases - your quality of life improves.
Some research suggests that regular strength training and aerobic exercise can help improve the thinking and learning skills of older adults.
Strength training can be done both at home and in the gym.
Strength training can be done:
- Using your body weight. For example - push-ups, sit-ups, planks, squats… A lot of different exercises that can be done without additional equipment and anywhere;
- Using resistance rubber. They are available at almost any sporting goods store with varying degrees of resistance;
- Using free weights. Weight bars and dumbbells are classic strength training tools. If you do not have weights at home, you can use any heavy object instead;
- Using exercise machines. Gyms offer a wide range of exercise equipment for all muscle groups;
- Using TRX. Very simple equipment - only 2 straps and practically unlimited training possibilities.
Strength training for the elderly
Weightlifting and stretching are useful at any age, but strength training is especially important for the elderly.
Why?
Because as we age, our strength decreases, our bones become more fragile, and our balance and joint mobility deteriorate. Strength training is a way to preserve youth, vitality, and beauty for longer.
You may no longer be able to perform all the same exercises and train as intensively as being younger. But you have to stay physically active because remember - if the muscles are not loaded, they will decrease.
And you become weaker, more fragile, more unstable…
Cardiovascular and respiratory system training
These are aerobic workouts or just "cardio". Cardio is very important for overall health because it trains our heart and respiratory system.
Adults need at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of high-intensity cardio activity per week.
Although many believe that aerobic exercise does not help build muscle, recent research show that they can promote skeletal muscle growth (hypertrophy). Aerobic exercise also increases overall fitness levels, which in turn reduces the risk of injury.
For optimal muscle building, aerobic exercise is recommended to perform:
- In the pulse range from 70% to 80% of the maximum heart rate;
- 30 to 45 minutes without interruption;
- 4 to 5 days a week.
Rest and muscle growth
Rest is an integral part of building muscle. By not allowing the muscles to rest, their ability to regenerate and grow is reduced. Insufficient rest also increases the risk of injury.
Don't "torture" your muscles - don't train the same muscle group for 2 or more days in a row. If you really want to train every day, train your legs one day, then your back the next, then your shoulders and arms…
The quality and duration of sleep are also important.
There are studies, showing that sleep deficiency reduces protein synthesis, promotes muscle loss, and inhibits muscle regeneration. However, further research is needed to confirm this connection.
Another research have shown that lack of sleep can increase the amount of cortisol (stress hormone) in the body, which can have a negative impact on muscle development.
Nutrition and muscle growth
Balanced and healthy diet is the main condition for maintaining physical fitness.
If you want to build/develop muscle, protein intake is especially important - about 1.5 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
The timing of protein intake is also important. It is believed that consuming 20 grams of protein during or immediately after exercise helps stimulate muscle protein synthesis, reduces protein breakdown, and promotes more efficient muscle regeneration.
The best sources of protein are:
- Meat;
- Fish;
- Eggs;
- Dairy products;
- Soybeans and tofu;
- Beans and lentils;
- Nuts;
- Seeds.
Tips for beginners
How to start?
If you want to train at home read - How to exercise and keep fit at home HERE.
If you want to go to the gym - at the beginning, it would be advisable to get acquainted with the equipment available in the gym with the help of a trainer and learn the proper exercise techniques. If you perform the exercises correctly, the workouts will be more effective and the results will be noticeable faster. And, not least, the risk of injury will be reduced.
Almost all gyms offer the first visit for free. In some, there are also full-time trainers who are obliged to introduce newcomers to the gym equipment.
Here are some more tips for beginners:
- Warm up for at least 5 to 10 minutes - walking or with any other aerobic activity. This will help to "warm up" the muscles and avoid injuries during training;
- Start with light weights;
- Increase your work weight gradually. The desired work weight is such that you can slowly perform the exercise 15 times in a row, but no longer 16 times;
- Try to control your movements as much as possible. If you feel that you are no longer able to perform the exercise accurately - it's time to rest;
- Exhale by lifting or pushing the weight, lowering - inhale;
- Don't worry about the pain and muscle fatigue that lasts a few days after your workout. If the muscle pain is very severe, it may be necessary to reduce the load;
- Cardio exercises (aerobic exercises) such as running, walking, and swimming can help build muscle. Of course, if they are done with the right intensity, duration, and frequency;
- Stick to a healthy, high-protein diet. If there is not enough protein in the body, the muscles will not grow. Animal products are rich in protein, but there are also several good sources of protein for those who do not eat meat..
Before you start your new and beautiful life, consult with your doctor or a professional trainer who will be able to assess your health and give recommendations on the optimal load and type of training.
Key takeaways
For your muscles to grow, you have to get them to adapt to a higher load level than they are used to. This can be achieved by increasing the working weights and/or constantly changing/modifying exercises.
The most important part starts after training - muscles recover and grow 24 to 48 hours after training. During this time, your muscles need to rest and get enough protein to regenerate and grow.
That's it. Good luck!
Sources:
Factors That Influence Body Weight
Real-Life Benefits of Exercise and Physical Activity
Re-examination of 1- vs. 3-Sets of Resistance Exercise for Pre-spaceflight Muscle Conditioning
Should men and women train differently?
Real-Life Benefits of Exercise and Physical Activity
Study of the Effect of Stress on Skeletal Muscle Function in Geriatrics
Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy after Aerobic Exercise Training
Effects Of Sleep Deprivation On Acute Skeletal Muscle Recovery After Exercise
Four Types Of Exercise Can Improve Your Health And Physical Ability
Share this article
Follow me on Facebook
I recommend reading these articles as well

Sugar - should you give it up when you lose weight?
I encounter many stereotypes on a daily basis, one of them - sugar is dangerous to health, it must be given up! So what exactly is the role of sugar in the diet and its role in the weight loss process?

How to exercise and keep fit at home
If you do not have the opportunity or the commitment to go to the gym - do it at home.

Split and Full Body workouts
Kas ir Split treniņš un vai tas ir labāks par Full Body treniņu? Kādas ir atšķirības un kādos gadījumos Jums piemērotāks ir Split un kādos – Full Body?

Sources of protein if we do not eat meat
I often get questions about the daily use of meat - so what to eat instead of meat to provide enough protein and other nutrients?